In a world where security is paramount, traditional access methods like keys, passwords, and ID cards are becoming outdated. They’re easily lost, stolen, or shared, creating vulnerabilities. Enter biometric access control, a powerful solution that uses a person’s unique biological and behavioural traits to verify their identity and grant access. This technology offers a higher level of security and accuracy because your biometric data is incredibly difficult to replicate.
These systems are widely used across various sectors, including government agencies, corporate offices, healthcare facilities, and airports, where protecting sensitive information and assets is critical.
How It Works
Biometric access control operates on a simple principle: you are your own key. When you first enroll in the system, a scanner or reader captures a unique physical or behavioral characteristic and creates a digital template from it. This template is then stored securely. When you later attempt to gain access, the system recaptures your biometric data and compares it to the stored template. If there’s a match, access is granted.
Common Biometric Methods
Biometrics can be broken down into different methods, each with its own specific way of identifying an individual.
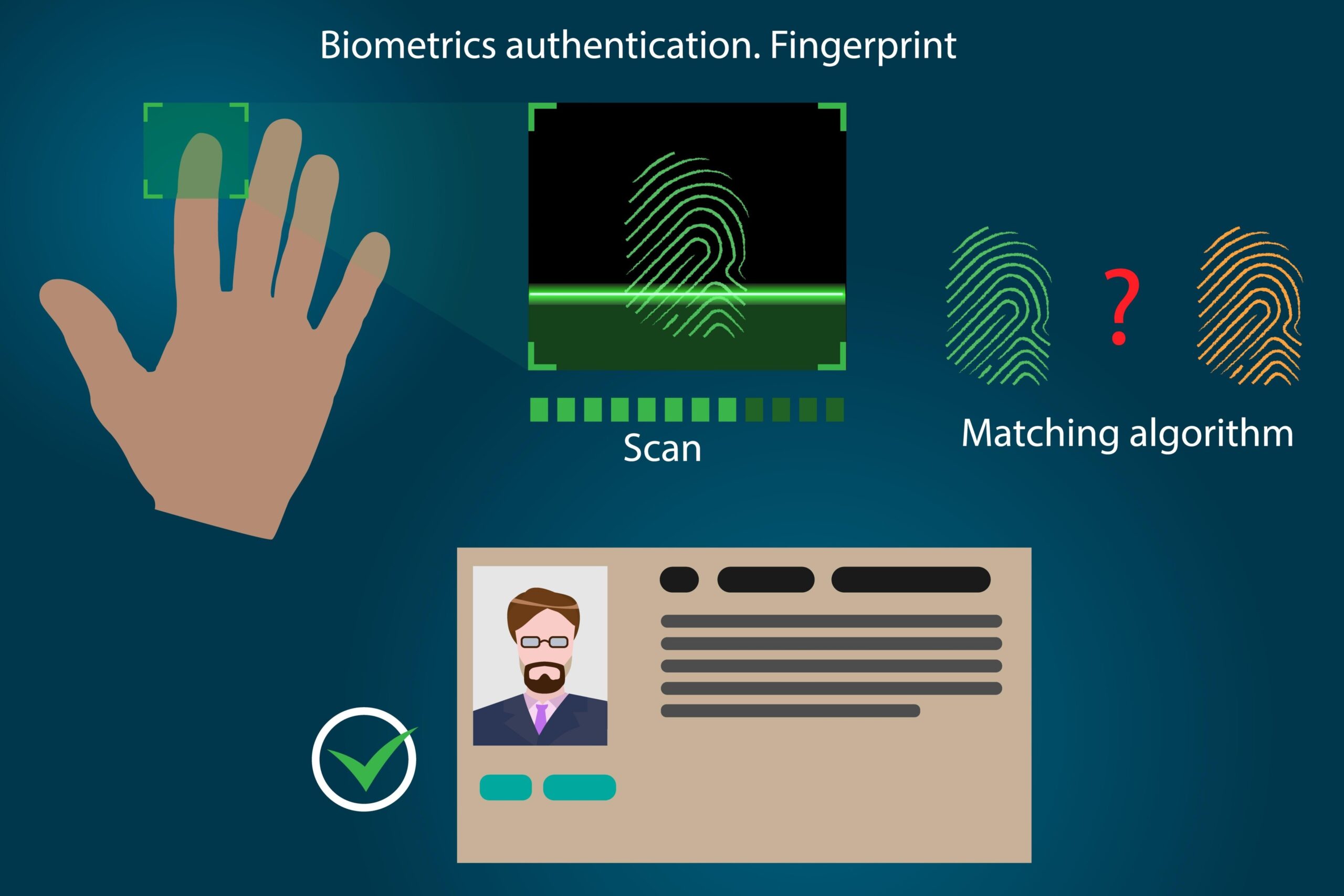
Fingerprint Biometrics
This is one of the most common and widely recognized forms of biometrics. The system captures the unique pattern of ridges and valleys on your fingertip and converts it into a digital template.
When you place your finger on the scanner, the system compares the new scan to the stored template to confirm your identity.
Iris Biometrics
Your iris, the colored part of your eye, has a distinct and complex pattern that remains stable throughout your life. A specialized camera captures this intricate pattern, and sophisticated algorithms compare the live image with a stored template.
Facial Biometrics
This method analyzes and measures unique facial features, such as the distance between your eyes, the shape of your nose, and the contour of your jawline. It creates a “faceprint” that can be used to verify your identity using either still images or video feeds.
Voice Biometrics
Instead of focusing on what you say, voice biometrics analyzes how you say it. It examines various vocal characteristics, including pitch, tone, and speech patterns, to create a unique voiceprint. This is then compared to an enrolled voiceprint to verify your identity.
Hand Geometry Biometrics
This method measures the size and shape of an individual’s hand, including the length and width of their fingers. A user places their hand on a reader, which then captures these measurements and compares them to the enrolled data for verification.
Biometric access control is revolutionizing security by offering a more reliable and sophisticated method of identity verification. By leveraging the unique physical and behavioural traits of individuals, these systems provide a powerful defense against unauthorized access. The widespread adoption of fingerprint, iris, facial, voice, and hand geometry biometrics across various industries underscores their effectiveness and growing importance. As technology continues to advance, we can expect biometric access control to become even more integrated into our daily lives, making our homes, workplaces, and data more secure than ever before. It’s a keyless, password-free future where you are your own best security measure.